When I first started working with design thinking and lean six sigma, I was having a tough time in understanding the difference between the two.
I was also struggling in understanding when to use either design thinking or lean six sigma, or if and how I could combine both to support me in my projects. After working with both I came to the following conclusion:
Design thinking focuses on uncovering and solving human centered problems using a designer’s perspective and toolkits. Whereas lean six sigma aims to deliver more customer value within a closed-end process, by providing consistent quality and by optimizing inefficiencies.
This is obviously just a rather simple way of distinguishing the two. In the next paragraphs you find more details on the differences and similarities, a deeper analysis of design thinking and lean six sigma, and lastly a best-practice on how to combine both to get even better results.
Design Thinking vs. Lean Six Sigma – Differences and Similarities
Design Thinking and Lean Six Sigma distinguishes themselves by trying to solve different types of problems.
Lean six sigma is a discipline which is focusing only on delivering more customer value by ensuring efficient operations, quality, and consistency. It is achieving this by focusing on making incremental and continuous improvements in a specific process.
Whereas design thinking is focusing on understanding and uncovering problems from a stakeholder using different perspectives. Which then result in a number of creative, drastic, radical and moonshot like ideas to solve a problem.
A similarity among both disciplines is the genuine use of brainstorming methods in order to produce ideas and in considering different perspectives. However, there are differences even here. Lean six sigma is focusing on ideas which are close to the problem at hand and eliminates the many innovative ideas that are seen as futuristic.
Design thinking on the other hand encourages future thinking, especially looking at new and at the first glance rather impractical ideas, which can then be seen as new problems to be solved in the future.
This is especially beneficial when trying to come up with creative ways to distinguish yourself from your competition.
Think of the Nintendo Switch, which was a completely different gaming console compared to the PlayStation for example, which has only focused on incremental improvements to their console’s technical capabilities over the past decades.

PlayStation 4 
Nintendo Switch
Common ground for design thinking and lean six sigma lays in the prototyping and testing phase after both disciplines have come up with concrete ideas to their problem.
Lean Six sigma and design thinking rely on experimentation and real user testing to verify if the solution is working properly or in the case of lean six sigma, if it is for example optimizing inefficiencies.
However, a major differentiator lays in the discipline’s consideration of the product life cycle. Design thinking does not look at the entire life cycle of a product or a solution, even though it does follow an iterative process. It rather picks out certain problems within the life cycle and tries to solve a concrete problem.
Whereas lean six sigma has the entire life cycle of a product or solution in mind and aims to optimize it to create more value for the customer.
The table below hopefully makes the difference between design thinking and lean six sigma easier to grasp:
| Design Thinking | Lean Six Sigma | |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Drastic, radical, unthought of and moonshot like changes and solutions | Incremental and continuous improvement |
| When to use it | Design thinking works best when you need to uncover problems which are badly defined or when you want to shine light on problems you haven’t even known existed. | Lean Six Sigma works best for specific and closed-ended processes which are causing inefficiencies |
| Used Methods | Design thinking incorporates hundreds of different techniques such as various brainstorming techniques, prototyping exercises, stakeholder mapping practices and much more. | Lean Six Sigma uses several techniques such as Value Stream Mapping (VSM), x-y matrixes to understand and optimize processes within a closed system. Lean Six Sigma also employs similar methods as design thinking when it comes to testing and prototyping. |
| Application | Design thinking would look at the problem of a fisherman who is trying to improve his fishing process by focusing on his specific needs and his problems, by coming up with various ideas using design thinking techniques, resulting in one or more solutions. These are then prototyped and tested until the best solution for a specific problem has been found. | Lean Six Sigma would pick out a specific process of the fisherman. Such as the delivery of the fish to his customers. It would then use certain techniques to uncover inefficiencies in the process such as steps where the transported fish cannot be moved due to the fisherman having to wait for the truck to pick up the fish, which reduces the freshness and therefore the quality of the fish. Lean Six Sigma would then encourage to brainstorm solutions for this specific problem so this process can become more efficient. |
Design Thinking in More Depth
Design thinking is a mind-set which follows a process and includes design thinking techniques focusing on putting the human in the center of a problem, when designing concrete solutions.
The concept exists because designers have a more creative way of thinking about problems. They are used to looking at ill-defined deeper gaps in the experience of a person.
Which helps them understand a problem from various perspectives such as the emotional side of how a person feels when encountering a problem.
In a business context, design thinking practitioners are focusing on finding solutions that are solving problems which at the same time should drive businesses value.
To solve a problem, the approach of design thinking is to first understand a problem from a user’s perspective, and then come up with many different ideas to solve the problem by analyzing the challenge/problem through different perspectives.
This requires patience and long-term commitment from designers, but also from the organization itself and their leaders.
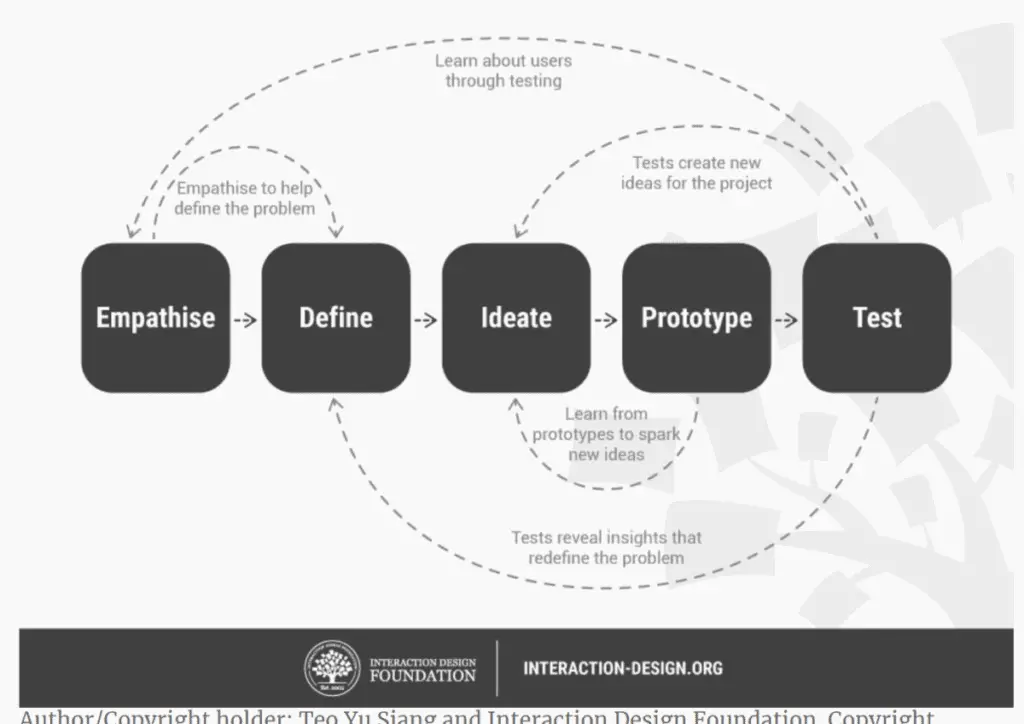
The reason is that the process of finding a solution using design thinking consists of five steps which are each encouraged to be undertaken.
The team at interaction-design has created a helpful illustration and an immensely in-depth article about design thinking:
To give you an example of how design thinking works in practice let’s look at the example of a product, which I’m sure you’re all familiar with or have at least seen in some tv commercials: Swiffer.
Swiffer is the cleaning solution from Procter & Gamble (P&G) and has been created following a designer’s approach of problem solving.
The designers back then actually went into people’s homes and watched how people cleaned their floors.
In doing so these designers asked many questions to understand the fundamental problem of cleaning floors. Which step is particularly frustrating and how are people actually cleaning their floors.
Turns out that the most annoying parts where the messiness and the time it took to sweep, but also how frustratingly time consuming it was to get the water, make the floor wet, and then drain the mob just to repeat the process again with fresh water.
By taking the time to dig deep into this problem with a designer’s perspective and then prototyping several different solutions. P&G managed to produce the Swiffer solution which combined sweeping and mopping while at the same time, eliminating the need for water.
This example shows that design-thinking is great in finding one concrete solution to a problem, but it does not consider the entire life cycle of a product.
What happens when a Swiffer breaks, what is the replacement and refund process and so on. This is where lean six sigma comes into play.
Lean Six Sigma: What is Lean and what is Six Sigma
The most crucial thing to understand about lean six sigma is that it aims on improving customer value through efficient processes and ensuring quality along the customer journey.
The word customer is here the most crucial. The idea is that lean six sigma tries to focus on providing value and quality for the customer – it is not aimed on providing value for the organization.
Of course optimizing processes and ensuring quality which makes the customer happy is a huge benefit for the organization in the long term, but lean six sigma is trying to make the experience for the customer, while he or she is engaging with the service or the product, as qualitative and as efficient as possible.
The discipline of lean six sigma consists however of two different parts: lean and six sigma.
Lean six sigma is in my opinion easier to understand ones you’ve understood lean, and six sigma as separate compontents first. So, let’s dive in.
Lean focuses on minimizing delays, errors and waste
As the headline already introduced the idea of lean is to minimize delays, errors, and waste in a specific process. To better grasp these three components let me explain them in a little more depth and with some examples:
Delays is examining processes such as sending in a broken computer. Lean would look at how long it takes send in the computer which usually takes around 2-3 days, then maybe around 2 – 4 hours of fixing the computer if it’s for example a simple hardware error, and then sending the computer back to the customer is estimated to take another 2 – 3 days.
Now what we find however is that this computer is sometimes just laying around for days or even weeks at the warranty center for whatever reasons. Which is obviously impacting the customer experience.
Lean tries do therefore shine light on this delay and to ultimately minimize the delay so the customer who sent in the computer receives it as quickly as possible.
Errors on the other hand is focusing mistakes created by the employees, the company or other factors which have a negative impact on the customer experience.
Personally, I ones ordered a computer when I was fifteen and got all excited because I wanted to set it up myself and everything. Only to discover that the hard drive (the thing where you save all the data) has had a technical error and didn’t function.
This can happen, but shouldn’t, since it gives the customer an annoying and irritating feeling. The guy who sold me the computer could have prevented this by simply checking the parts of the computer if they function before selling it to me.
This was a rather simple example where an error only causes frustration, think of a scenario of an airplane pilot making an error while attempting to land, such as forgetting to extract the wheels.
Quite a different story and impact on the customer experience indeed. Which is why airline companies are trying hard to minimize errors by letting pilots go through several years of challenging training in order to receive a pilot’s license.
Lastly, we have the matter of waste. The idea of waste within the context of lean is focusing on products or a service which are thrown away or are discarded because they lacked the quality to make it through quality control.
Let me give you a concrete example about my first summer job when I was fifteen. I was working in a local plastics factory where they’d produce car cockpits where all the information such as speed and your current gas level is displayed for the driver of the car.

They’d produce thousands of these cockpits with hundreds of them not passing quality control due to scratches inside the cockpit, or some other weird oddities which occurred during the production.
This was an immense waste of resources for the company, which could have been avoided by improving for example the production line by educating the workers to be more careful with the pieces to avoid scratches and such.
This was the idea of lean with it’s the elements delays, errors and waste. Let’s now have a closer look at the six sigma.
Six Sigma Focuses on Quality and Consistency
In contrary to lean, six sigma focuses only on quality and consistency. Again, from the perspective of a customer. Which means six sigma tries to ensure that the customer who purchased the service always receives a consistent experience and an excellent product or service.
My personally favorite ice cream is a really good example of ensuring quality and consistency throughout the years of purchasing a product from them: Ben & Jerry’s.
Their quality control process starts with the “cow” from where they receive the milk in order to produce their ice cream. They ensure through their quality check that for example no allergic ingredients are somehow mixed up in the allergy friendly products.
They are able to do this by sourcing all of their resources locally and going through a thorough analysis for pathogens and other tests to meet specific guidelines.
To ensure for example that the “Cookie Dough” ice cream (my absolute favorite) has enough “chunks” they analysis the products using lots of computer data or they literally pull several samples from the production line, cut them in half and count the number of chunks manually.
The end result is that the customer will always have the same qualitative experience throughout the years of purchasing Ben & Jerry’s ice cream.
This is what six sigma is focusing on. In combining lean and six sigma you receive a discipline and a method which focuses on improving customer value by more efficient processes and ensuring consistent quality.
Combining Design Thinking and Lean Six Sigma
Design thinking and lean six sigma are different disciplines, which can bring an immense value when applied together.
If you’re for example starting a business you could use design thinking methods on a higher level, to understand or uncover ill-defined or unknown problems, which could then be translated into creative solutions using design thinking techniques.
In the second step, after you have launched your product you could use lean six sigma to optimize the customer experience by minimizing delays, errors and waste but also by ensuring quality and consistency.
To wrap this up.
I hope this article helped you understand and grasp the difference between lean six sigma and design thinking. But also how you could make use of both of them in the most effecitve and efficient way.

